Spectacular Tips About When To Use A Histogram Vs Bar Graph Create Secondary Axis In Excel

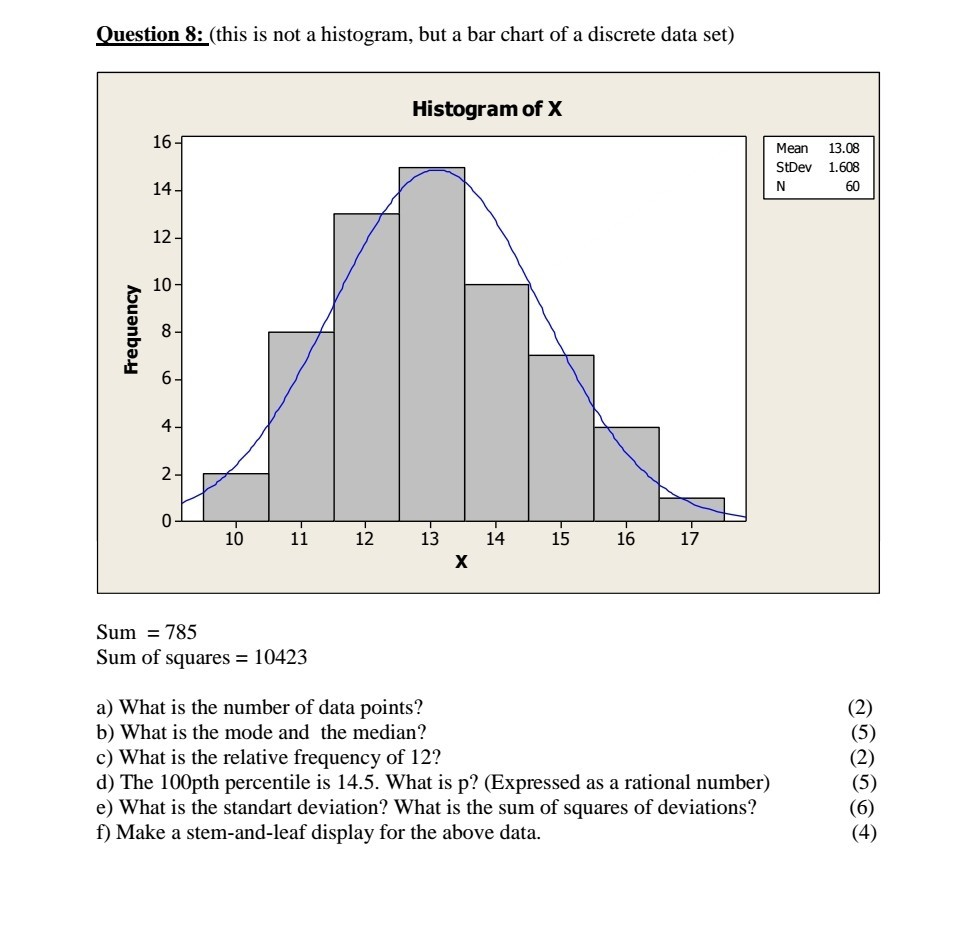
Histograms are used to show averages.
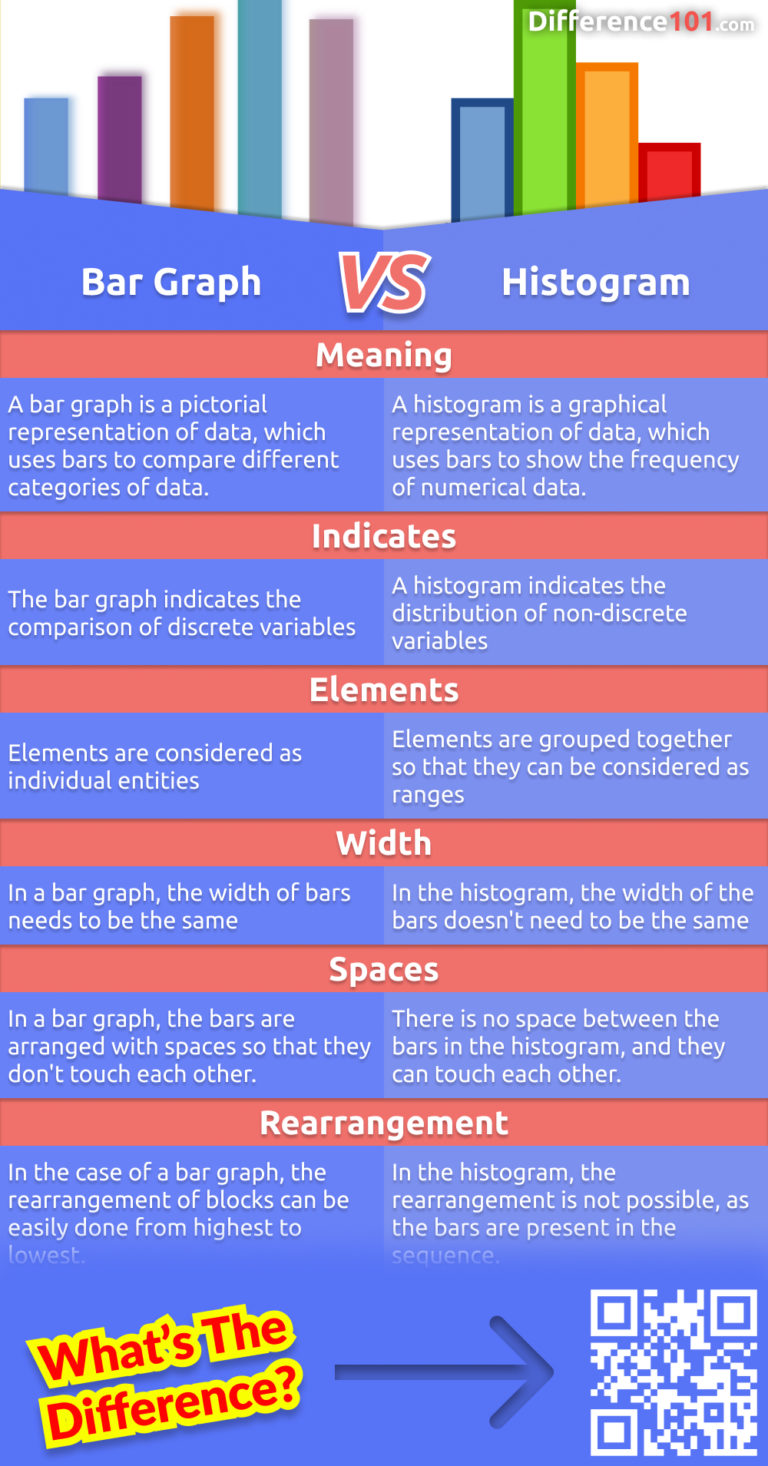
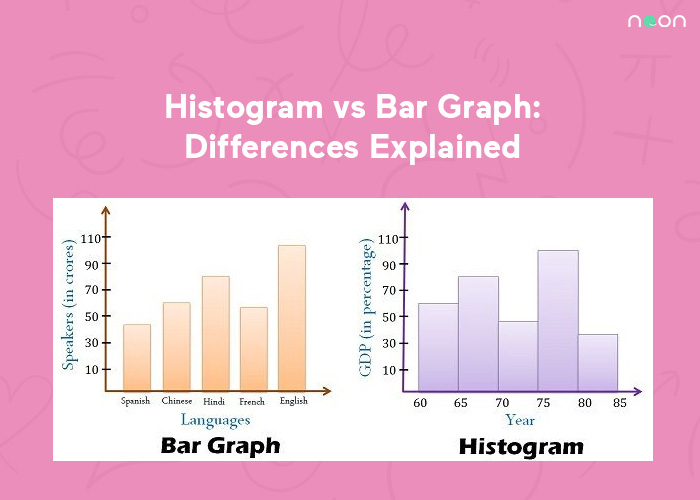
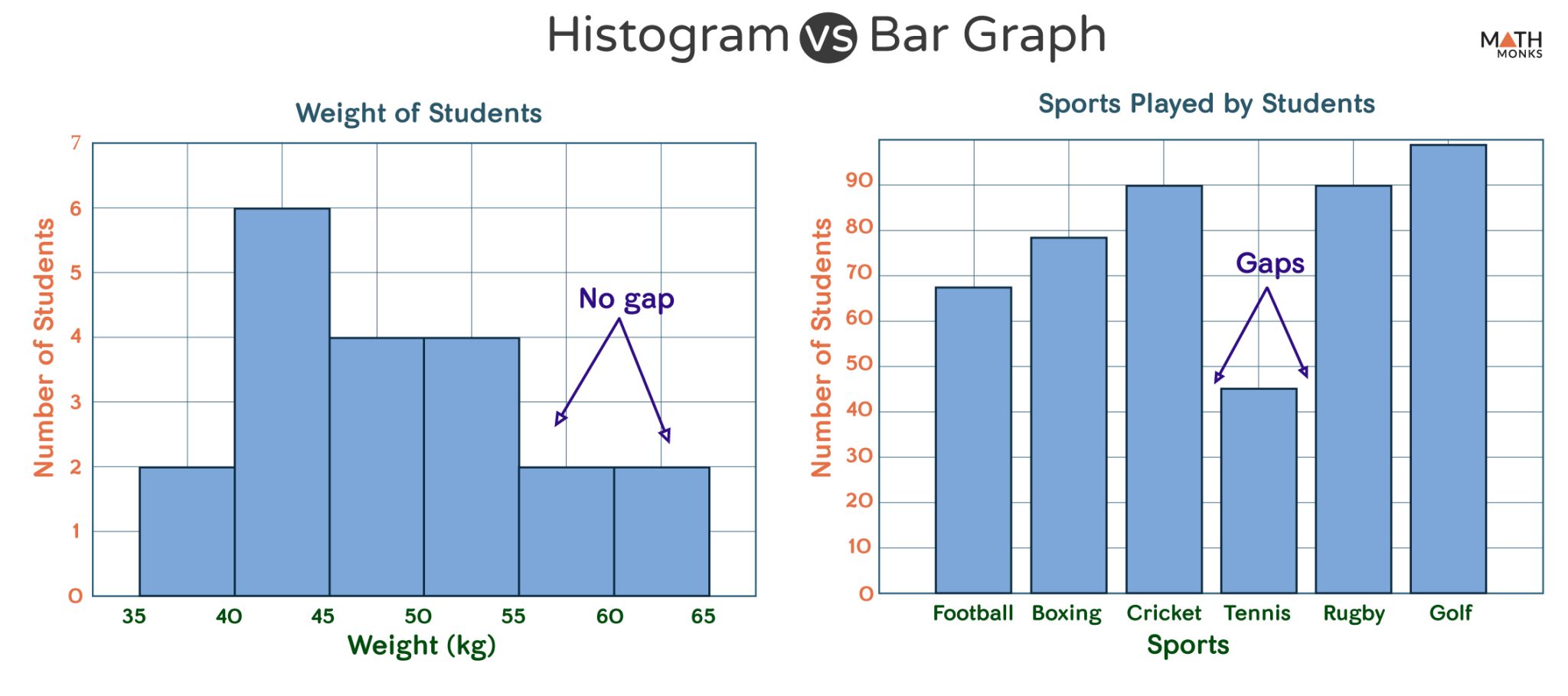
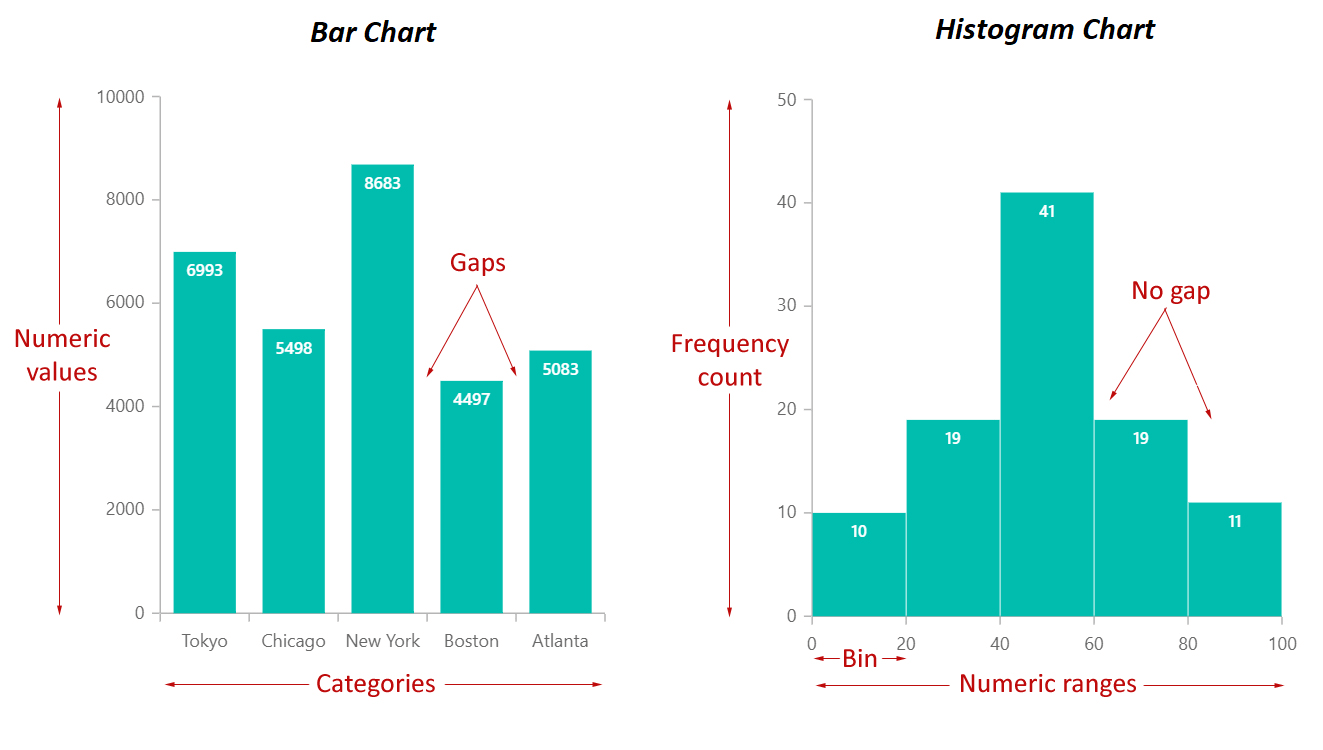
When to use a histogram vs bar graph. As the data’s in a range, putting them into a histogram makes it easy to see which values come up most often. A bar chart displays categorical data with space between the bars, ideal for comparing distinct items. In the histogram, the bars are adjacent to each other.
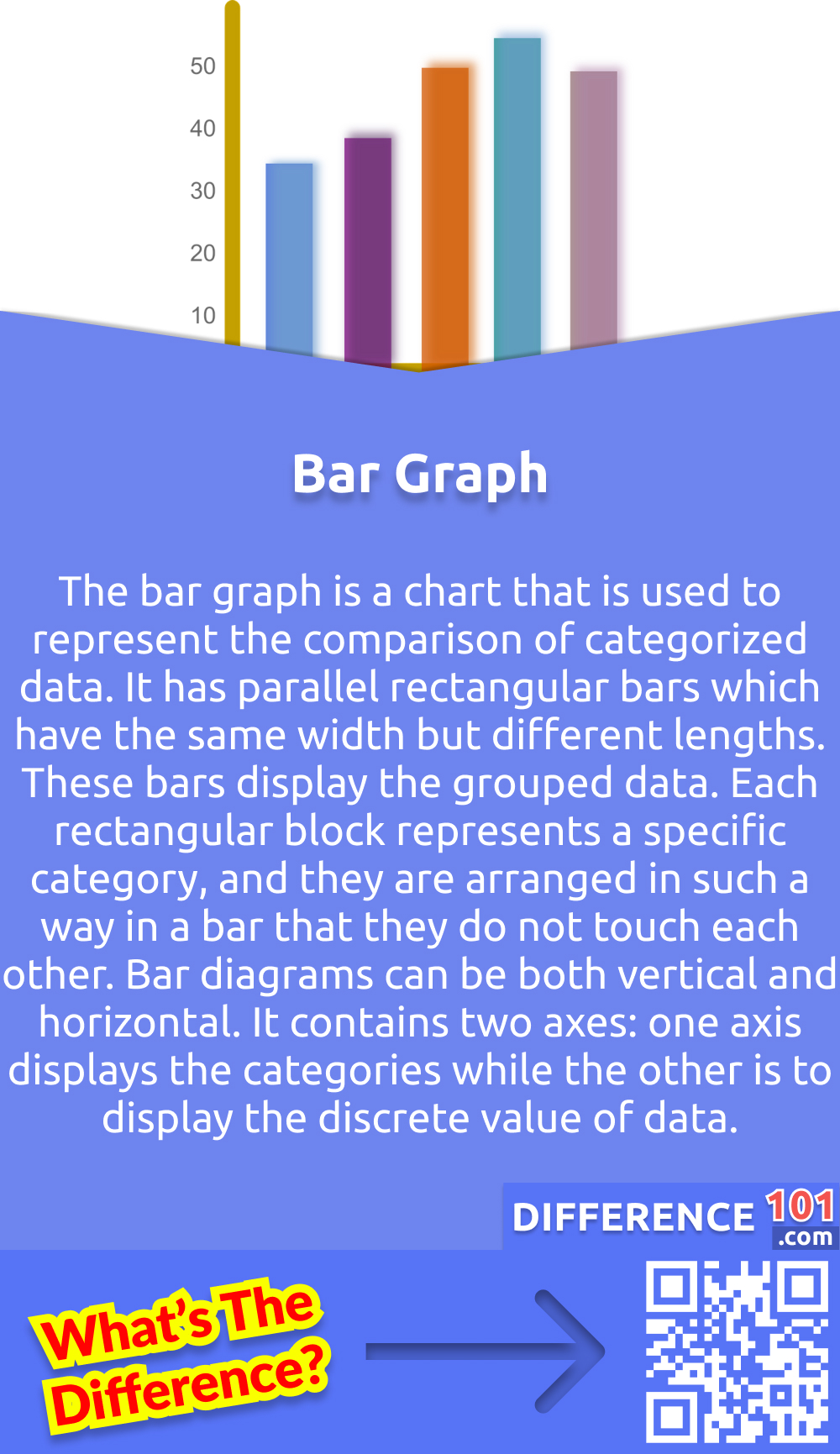
To keep the answer simple: Conversely, a bar graph is a diagrammatic comparison of discrete variables. Bar chart categories are qualitative, which means you can't count them numerically.
Bar graphs are the ideal type of graph to compare data between different categories. The histogram refers to a graphical representation that shows data by way of bars to display the frequency of numerical data whereas the bar graph is a graphical representation of data that uses bars to compare different categories of data. Putting data into bar graph form makes it easy to see which value is larger and by how much.
Bar graphs are less sensitive to the choice of intervals or bins, while histograms require careful consideration of bin size. When should i use a bar chart? For continuous data and distribution analysis, use a histogram.
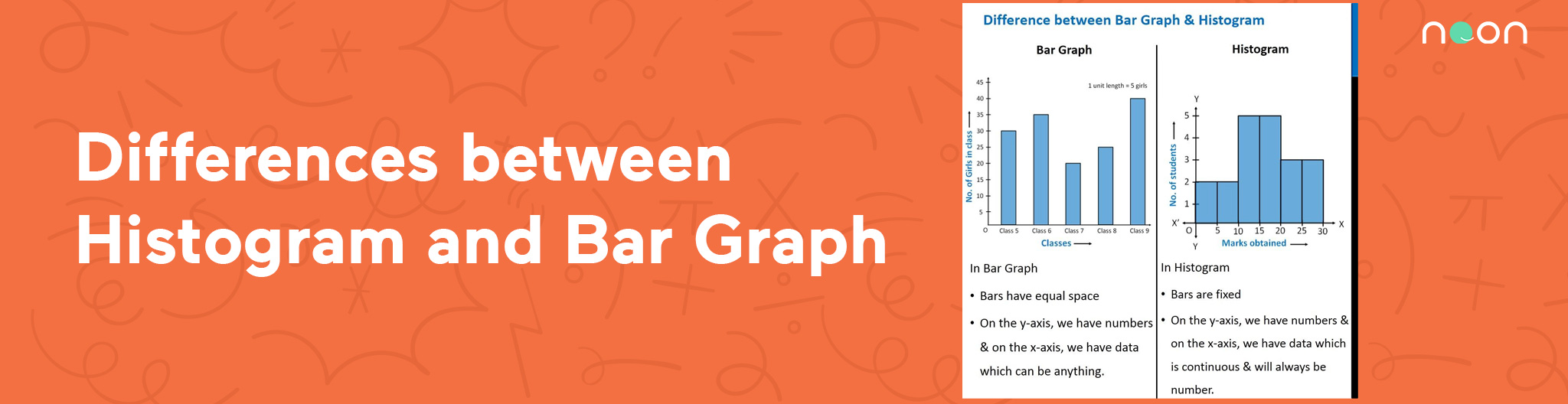
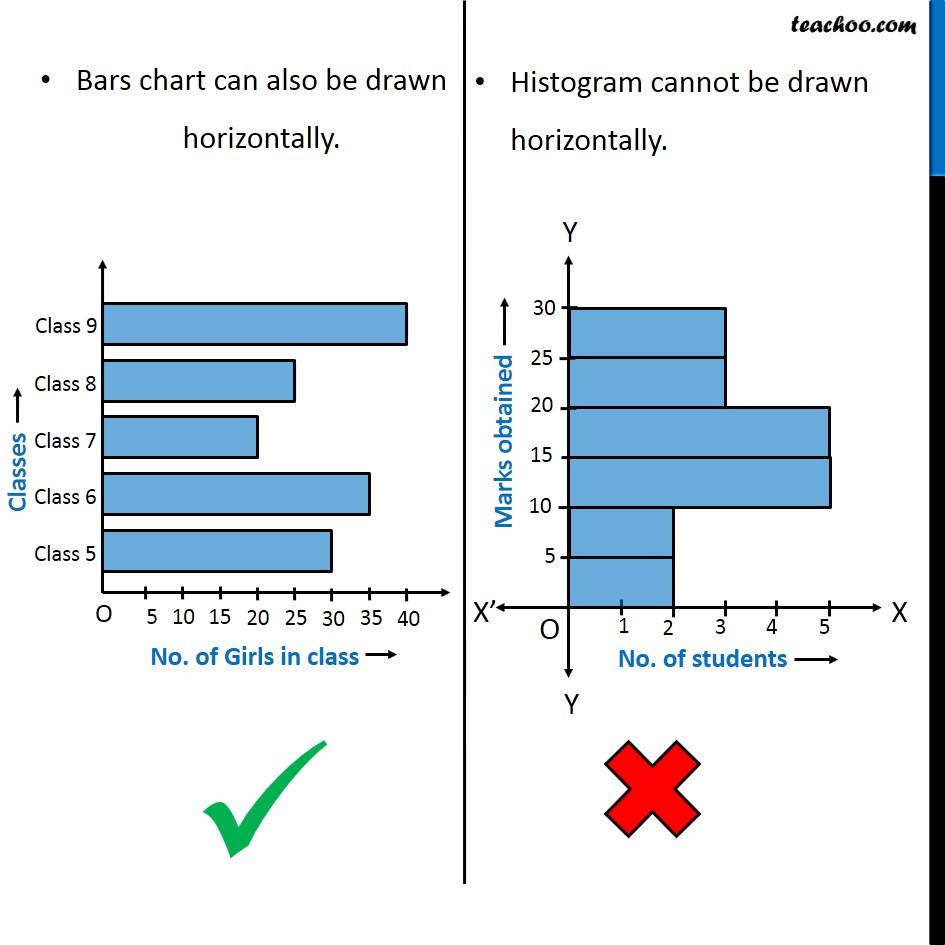
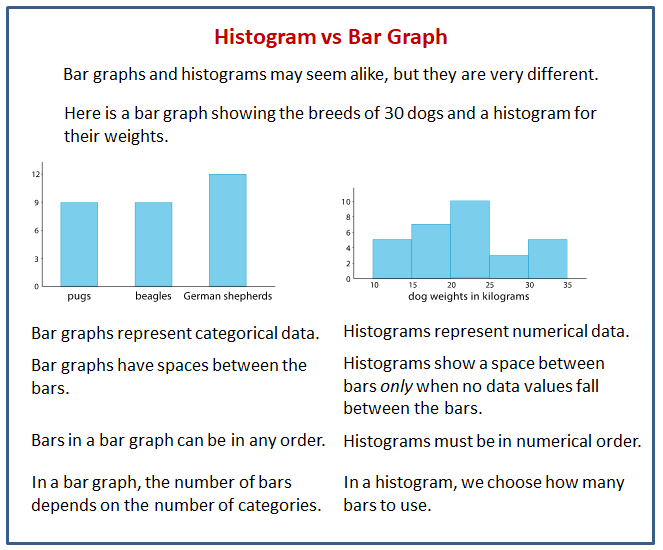
While the bars on a bar chart are separate categories of items, the bars on histograms are intervals (or bins) that span from one number to another. When would you use a bar graph rather than a histogram? Bar graphs are used to compare discrete or categorical variables, while histograms are used to visualize quantitative data and represent the frequency of the data in a dataset.
Here are some of the key differences between bar charts and histograms: Bar graphs compare categorical data with rectangular bars. Histogram bars touch each other, highlighting continuous data.
Bar charts should be used to explain how much stuff there is in different categories, and categories are qualitative. Let’s begin by defining each term to pave the way for a. While they may appear similar initially, both serve different purposes and are best suited for.
Histograms display frequency distributions of continuous data sets. Bar graphs are used for comparison purposes. Bar graph bars are separated, emphasizing distinct categories.
A histogram represents the frequency distribution of continuous variables. Unlike histograms, the bars in bar charts have spaces between them to emphasize that each bar represents a discrete value, whereas histograms are for continuous data. Histogram and bar graph allow you to visualize the distribution of your data and gain valuable insights into its patterns, trends, and outliers.
Read on to learn the definition and potential uses of each and their associated advantages and disadvantages. Histograms are best for looking at the frequency of data values within a single dataset. The key difference between the two is that the bars in a bar graph represent individual categories, while the bars in a histogram represent ranges of values.

.jpg)



.png)